Ethereum Gas Fee Optimization Strategies for 2025

Ethereum gas fees have remained a persistent challenge for users throughout the network’s evolution, with transaction costs continuing to fluctuate based on network congestion and demand patterns. Understanding how to minimise these expenses has become crucial for anyone interacting with the Ethereum ecosystem, whether for DeFi trading, NFT transactions, or smart contract interactions. The landscape of gas fee optimisation in 2025 offers numerous strategies and technological solutions that can deliver substantial savings for both casual users and power traders.
Ethereum Gas Fees in 2025
Ethereum gas fees represent the computational cost required to execute transactions and smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. These fees serve as compensation for validators who process and secure network transactions. Ethereum ETF Inflows are determined by the network’s demand and the complexity of transactions. The fee structure comprises a base fee that is burned and a priority fee that is allocated directly to validators, resulting in a dynamic pricing mechanism that responds to network conditions.
Key factors affecting gas fees include:
- Network congestion levels during peak trading hours.
- Transaction complexity and smart contract interaction requirements.
- DeFi protocol activity and automated trading volumes.
- NFT minting events and marketplace transactions.
- Major market movements are triggering increased trading activity.
- Time-of-day and day-of-week patterns in network usage.
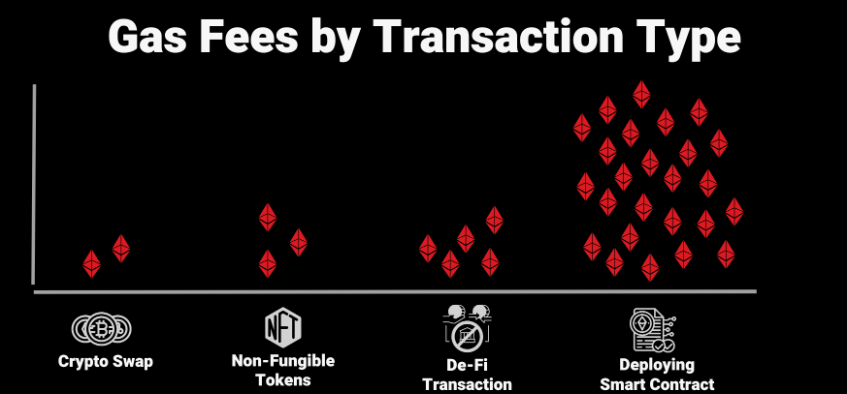
Network congestion remains the primary driver of elevated gas fees, with prices typically spiking during periods of high DeFi activity, NFT launches, or major market movements. Complex smart contract interactions require more computational resources and, therefore, incur higher fees compared to simple token transfers.
The implementation of Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559 has introduced more predictable fee structures, but significant cost variations persist based on network utilisation patterns. Users can leverage gas fee prediction tools and monitoring services to identify optimal transaction timing and minimise costs through strategic planning.
Layer 2 Solutions: The Primary Cost Reduction Strategy
Layer 2 solutions offer the most significant gas fee savings in 2025, enabling users to unlock savings of 80-99% on gas fees for most transactions by bridging their assets to these scaling solutions. The three dominant Layer 2 platforms each offer distinct advantages for different use cases and user preferences.
Popular Layer 2 solutions include:
- Arbitrum: Optimistic rollup technology with a comprehensive DeFi ecosystem.
- Optimism: Developer-focused rollup with retroactive public goods funding.
- Polygon: Sidechain solution offering fastest speeds and lowest fees.
- Base: Coinbase-backed Layer 2 with growing institutional adoption.
- zkSync: Zero-knowledge rollup with enhanced privacy features.
- StarkNet: Cairo-based zkSTARK technology for complex computations.
Arbitrum has emerged as a leading Layer 2 solution utilising optimistic rollup technology to process transactions off-chain before settling on the Ethereum mainnet. The platform supports a comprehensive ecosystem of DeFi protocols, including Uniswap, SushiSwap, and Curve, enabling users to access familiar applications at dramatically reduced costs. Arbitrum’s compatibility with existing Ethereum tooling means that users can interact with dApps using the same wallets and interfaces they’re accustomed to on the mainnet.
Optimism represents another major optimistic rollup solution that emphasises developer experience and ecosystem growth through its retroactive public goods funding model. The platform has attracted significant DeFi activity and offers comparable gas savings to Arbitrum while maintaining strong security guarantees through its connection to the Ethereum mainnet. Optimism’s focus on public goods and developer incentives has created a vibrant ecosystem of innovative applications.
Polygon operates as a sidechain solution, providing the fastest transaction speeds and lowest fees among the major Layer 2 options. While technically not a true Layer 2 due to its separate consensus mechanism, Polygon offers exceptional user experience with near-instant confirmations and minimal transaction costs. The platform’s extensive DeFi ecosystem and enterprise partnerships make it attractive for both retail and institutional users.
Strategic Transaction Timing and Optimisation
Gas fees vary significantly based on network congestion, with users able to save money by transacting during off-peak hours when the network has fewer active users. Weekend periods and late-night hours typically offer the lowest gas prices as business and trading activity decrease.
Effective timing strategies include:
- Weekend transactions: Saturdays and Sundays typically show 20-40% lower fees.
- Late-night hours, 2-6 AM UTC, often provide optimal pricing windows.
- Holiday periods: Major holidays are associated with reduced business activity and lower fees.
- Pre-market hours: The early morning period before US trading sessions begin.
- Gas price monitoring: Using real-time tracking tools for optimal timing.
- Transaction scheduling: Planning non-urgent transactions for low-fee periods.
Advanced users can optimise their transaction parameters by carefully setting the gas limit and gas price in wallets like MetaMask. Setting lower gas prices during periods of reduced network activity can result in successful transactions at substantially reduced costs; however, users must balance these savings against potential delays in transaction confirmation.
Transaction batching represents another effective strategy, allowing users to combine multiple operations into a single transaction to minimise overall gas consumption. This technique proves particularly valuable for users who regularly interact with DeFi protocols or manage multiple token positions.
Gas token strategies, while more complex to implement, can provide additional savings for sophisticated users. These mechanisms involve purchasing and storing gas during low-fee periods, then utilising the stored gas during high-fee periods to reduce transaction costs. However, the effectiveness of gas tokens has diminished following certain Ethereum upgrades, making this strategy less viable than previously.
DeFi Protocol Selection and Fee Optimisation
Different decentralised exchanges and DeFi protocols exhibit varying levels of gas efficiency, making protocol selection an important consideration for cost-conscious users. Automated market makers like Uniswap V3 have implemented concentrated liquidity features that can reduce gas costs for certain types of trades, while aggregators like 1inch optimise routing to minimise both slippage and gas fees.
Gas-efficient DeFi protocols include:
- 1inch: DEX aggregator optimising for the lowest combined cost and slippage.
- Uniswap V3: Concentrated liquidity reduces gas costs for active traders.
- Curve Finance: Specialised for stablecoin swaps with minimal slippage.
- SushiSwap: Community-driven DEX with competitive gas optimisation.
- Balancer: Automated portfolio management with gas-efficient rebalancing.
- Paraswap: Multi-DEX aggregator focusing on optimal routing.
- Kyber Network: Dynamic market making with gas cost considerations.
Users can reduce gas fees when swapping tokens by using decentralised exchanges with optimised fees, leveraging Layer 2 networks, or scheduling swaps during low-traffic periods. Protocol-specific optimisations, such as using limit orders instead of market orders, can also contribute to overall cost reduction.
The emergence of gasless transaction protocols represents a significant development in fee optimization, allowing users to pay transaction fees using the tokens they’re trading rather than requiring ETH holdings. These meta-transaction solutions shift the responsibility for gas payments to third parties or integrate fee payments into the transaction itself.
Alternative Blockchain Considerations
Some users explore alternative blockchains with different fee models and faster block times, such as Avalanche, which offers lower costs and near-instant confirmations, or Binance Smart Chain, which features lower fees and EVM compatibility. These alternatives can solve high-fee problems but require users to bridge assets and adapt to different ecosystems.
Popular Ethereum alternatives include:
- Avalanche: Sub-second finality with C-Chain EVM compatibility.
- Binance Smart Chain: Lower fees with a centralised validator model.
- Fantom: High-speed transactions with Opera network architecture.
- Solana: High-throughput blockchain with a different programming model.
- Cardano: Proof-of-stake with native token support.
- Algorand: Pure proof-of-stake with instant finality.
- Cosmos: An Interoperable blockchain ecosystem with custom chains.
Ethereum-compatible chains, such as Avalanche C-Chain and Fantom, offer familiar development environments and tooling while providing significantly lower transaction costs. However, users must consider factors such as network security, decentralisation, and ecosystem maturity when evaluating these alternatives.
Cross-chain bridges enable the movement of assets between different blockchain networks, allowing users to access lower-fee environments while maintaining exposure to their desired protocols and tokens. The bridge landscape continues to evolve with enhanced security measures and improved user experience.
Wallet Configuration and Gas Management
Modern cryptocurrency wallets provide sophisticated gas management features that enable users to optimise their transaction costs. MetaMask’s advanced gas controls allow users to set custom gas limits and prices, while newer wallets like Rabby and Frame provide enhanced gas estimation and optimisation features.
Essential wallet features for gas optimisation:
- Custom gas settings: Manual control over gas price and limit parameters.
- Gas estimation tools: Real-time fee predictions and recommendations.
- Transaction queuing: Ability to schedule transactions for optimal timing.
- Multi-network support: Seamless switching between mainnet and Layer 2s.
- Fee history tracking: Analysis of past transactions for optimisation insights.
- Speed vs. Cost Options: Preset Configurations for Different Urgency Levels.
- Batch transaction support: Combining multiple operations to reduce costs.
Hardware wallet integration adds security layers while maintaining gas optimization capabilities. Ledger and Trezor devices support Layer 2 networks and provide secure transaction signing for cost-optimised transactions across multiple networks.
Gas fee prediction tools and browser extensions can provide real-time insights into optimal transaction timing. Services like GasNow, ETH Gas Station, and Blocknative’s Gas Platform offer detailed analytics and recommendations for cost-effective transaction scheduling.
Future Developments and Ethereum 2.0 Impact
Ethereum 2.0 is expected to significantly lower gas fees by increasing the network’s capacity to handle transactions, with enhanced throughput and efficiency from sharding and other upgrades aiming to reduce transaction fees to less than $0.001. These improvements will make Ethereum more accessible and cost-effective for a broader range of use cases.
Expected Ethereum 2.0 improvements include:
- Sharding implementation: Parallel processing across multiple chains.
- Proto-danksharding: Reduced data availability costs for Layer 2s.
- Account abstraction: Flexible gas payment mechanisms and sponsored transactions.
- Improved validator efficiency: Lower computational overhead for consensus.
- Enhanced MEV protection: Reduced front-running and sandwich attacks.
- Cross-shard communication: Seamless asset transfers between shards.
- Upgraded virtual machine: More efficient smart contract execution.
The transition to proof-of-stake consensus has already begun to impact network efficiency, with future upgrades, including sharding, expected to provide significant scalability improvements. Ethereum Outpaces Proto-danksharding and full danksharding implementations will specifically target Layer 2 data availability costs, further reducing fees for rollup-based solutions.
Account abstraction features being developed for Ethereum will enable more sophisticated gas payment mechanisms, including sponsor-paid transactions and more flexible fee structures. These developments will improve user experience while providing additional avenues for cost optimisation.
